 In depth study of the principles of metals
and metal shaping In depth study of the principles of metals
and metal shaping
1. Structure of metals, language of metals from the “inside” (atomic theory)
- Periodic chart – metals/gas/metalloids – valance rings – inert gases
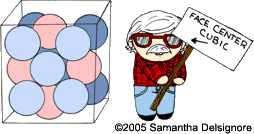 Molecules vs. lattice patterns FCC BCC CPH Molecules vs. lattice patterns FCC BCC CPH
Gas/liquid/solid – lattice dendritic growth – crystals/grain
Size of crystal/grain correlated to strength
- Slip planes movement – twinning in CPH
- Lattice defects – point – vacancies and interstitial atoms – line- planes of atoms – dislocation and stacking faults (edge and screw)
- Strengthening mechanisms – tensile strength – temper designation – appropriate welding rod – how alloys work for added strength
 Strain hardening/work hardening/age hardening – creep – use up slip planes – traffic jams – alloy atoms substitutions – interstitial Strain hardening/work hardening/age hardening – creep – use up slip planes – traffic jams – alloy atoms substitutions – interstitial- Recrystallization – anneal aluminum 600 degree F/copper – 400 degree F/iron 850 degree F.
2. The way metals are smelted, numbered, produced/heat treated/strengthened
- Structure of steel – basic carbon range 008% – .8% carbon, ferrite/pearlite – low/medium/high carbon steels – when to use what steel – micrograph view, iron/carbon phase diagram, numbering systems AISI, SAE, ASTM
- Tool steel/cast iron – letter/number designation – cast iron 2%+ carbon – how steel is made – killed, semi-killed, capped, rimmed – how to purchase: hot roll, P&O, cold roll – relationship temperature to color – how heat treated
 3. Specific principles of how a compound curve is developed from flat sheets, shrinking/stretching, plastic deformation, understanding strain concentrations 3. Specific principles of how a compound curve is developed from flat sheets, shrinking/stretching, plastic deformation, understanding strain concentrations
- Elastic limit – above/below – pushing /pulling – compression/tension – concentrating forces – more atom movement – not all shaping is the same
- Shape and form – shrinking/stretching, folding – paper patterning, false shrink/false stretch. What is a “dent”? How to apply to parts being made.
- Compound curves – demonstration of shaping 4 panels to illustrate what a compound curve is – the shapes: high crown, low crown, reverse curve.
- Shrinking – cold shrinking: demonstration with claw hammer – using tuck tool, power equipment, hot shrinking: torch and friction blade – what happens to metal on atomic level – how stresses are induced and removed
- Stretching- concept of maximum die contact – planishing – radial and linear – radius and flats – standard compound curves – reverse curves
4. Introduction & practice on power equipment
- Stretching & shrinking – air hammer, Pullmax, power hammer (Yoder), wheeling machine.
Day 1 Day 2 Day 3
|